Patients’ preference for different tonometers in a tertiary ophthalmic clinic
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Intraocular pressure measurement is a routine examination in the Eye clinic, and it is essential in the management of glaucoma.
Aim: To assess the preference of patients for three different types of tonometers used at the Eye clinic of the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital, Port Harcourt, Nigeria.
Methods: This was a comparative cross-sectional study of adults 18 years and older. Their intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured using Perkins applanation tonometer (PAT), Pulsair non-contact tonometer (NCT) and iCare rebound tonometer (RBT). Their preferred tonometer and reasons for their choices were elicited.
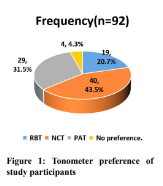
Results: There were 69 (75%) male and 23 (25%) female respondents in the study. The mean age was 38.84±13.34 years, with an age range of 18 - 71years. Majority of participants preferred the NCT (43.4%, 40), followed by PAT (31.5%, 29 while the RBT (20.7%,19) was the least favourite instrument and 4.4% of participants had no preference. There was a statistically significant difference in the preference of the three tonometers, P value = 0.004 (<0.05). With the iCare, most participants preferred it for the following reasons - no pain or discomfort (n=5; 26.3% each) and no eye drops (26.3%). With the NCT, the reasons given were speed (n=7; 17.5%), no pain (37.5%) and no eye drops (10%). For the PAT, the commonest reason for preference was no pain (65.5%).
Conclusion: Majority of the participants in this study preferred the NCT, followed by the PAT and RBT tonometers respectively.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1. Sofi RA, Shafi S, Qureshi W, Ashraf S. Merits of treabeculectomy in advanced and end stage glaucoma. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 2018; 12(2):57-60.
2. Farhood QK. Comparative evaluation of intraocular pressure with an air-puff tonometer versus a Goldmann applanation tonometer. Clin Ophthalmol 2013; 7: 23–27.
3. Mohan S, Tiwari S, Jain A, Gupta J, Sachan SK. Clinical comparison of Pulsair non-contact tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometer in Indian population. J Optom 2014; 7(2): 86–90.
4. Babalola OE, Kehinde AV, Iloegbunam AC, Akinbinu T, Moghalu C, Onuoha I. A comparison of the Goldmann applanation and non-contact ( Keeler Pulsair EasyEye ) tonometers and the effect of central corneal thickness in indigenous African eyes. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2009; 29(2): 182–188.
5. Vernon SA. Non-contact tonometry in the postoperative eye. Br J Ophthalmol 1989; 73(4): 247–249.
6. Yilmaz I, Altan C, Aygit ED, Alagoz C, Baz O, Ahmet S, et al. Comparison of three methods of tonometry in normal subjects: Goldmann applanation tonometer, non-contact airpuff tonometer, and Tono-Pen XL. Clin Ophthalmol 2014; 8: 1069–1074.
7. Ademola-Popoola DS, Odi AF, Akande TM. Comparison of IOP readings using
rebound iCare tonometer and Perkins applanation tonometer in an African population. J West Afr Coll Surg 2014; 4(1): 17–30.
8. World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013;310(20):2191-2194.
9. Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM, Pfeiffer N, Thieme H. Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2008; 246(6): 875–879.
10. Krakau CE, Wilke K. On repeated tonometry. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh)1971; 49(4): 611–614.
11. Moses RA, Liu CH. Repeated applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 1968; 66(1): 89–91.
12. Tamçelik N, Atalay E, Cicik E, Özkök A. Comparability of Icare Pro Rebound Tonometer with Goldmann Applanation and Noncontact Tonometer in a Wide Range of Intraocular Pressure and Central Corneal Thickness. Ophthalmic Res 2015; 54(1): 18–25.
13. Adebayo DI. Intraocular pressure measurements using Goldmann and Non Contact tonometers in glaucoma and non glaucoma patients in a nigerian Military Eye centre. Unpublished Fellowship dissertation (FMCOphth). National Post Graduate Medical College of Nigeria. 2016; 43–44.
14. Kontiola A, Puska P. Measuring intraocular pressure with the Pulsair 3000 and Rebound tonometers in elderly patients without an anesthetic. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004; 242: 3–7.
15. Pakrou N, Gray T, Mills R, Landers J, Craig J. Clinical Comparison of the Icare Tonometer and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry. J Glaucoma 2008 ;17(1):43-47.