Staging and grading chronic viral hepatitis: A teaching hospital experience using an objective histological activity index in a tropical population
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Chronic viral hepatitis (CVH) is the leading cause of chronic liver diseases (CLD) and exhibit diffuse parenchymal damage requiring a systematic assessment of disease extent and progression.
Aims: The aim of this study is to determine the epidemiological pattern and grade/stage all cases of CVH using Ishaq Modified Histologic Activity Index (HAI); then share and to compare our experience with similar works elsewhere.
Methods: Ten years (2006–2015) liver biopsies received in the Department of Pathology, Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital Zaria, were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin and stained with routine and special stains were reviewed, graded and staged using Ishaq HAI. Data were analysed and presented in statistical frequency distribution tables and figures.
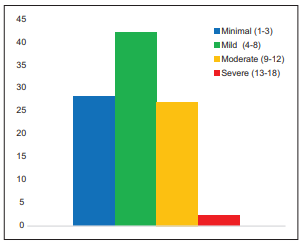
Results: CVH formed 55.2% was the most common of liver diseases. There were119 male and 47 female with male-to-female ratio of 2.5: 1 and peaked in the third decade of life. Nearly 42.2% had modified Ishaq HAI score of 4–8, while 28.3% and 27.1% had score 1–3 and score 9–12, respectively. Only 2.4% had score of 13–18. Nearly 70.5% of cases were between Stages 0 and 2, 25.9% of cases were Stage 3and 4 while only 6% were in Stage 5. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) was the most common aetiology and found in 77.7% of cases, 13.3% were associated with hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HBV/HCV co infection in 9.0%.
Conclusions: CVH was the most common form of CLD, peaked in the third decade of life. Nearly 42.2% were in mild grade disease while 70.5% had Stage 2 and below disease. HBV infection was the most common aetiology.
Downloads
Article Details
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1. Hepatitis B vaccines. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2004;79:255‑63.
2. Sherlock S, Dooley J. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 11th ed. Philadelphia: WB. Saunders Co. p. 286‑99.
3. Valente F, Lago BV, Castro CA, Almeida AJ, Gomes SA, Soares CC, et al. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of hepatitis B virus in Luanda, Angola. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2010;105:970‑7.
4. Omolade A, Fred J, Abdulkareem FB, Olusegun O. The clinical laboratory and the diagnosis and management of chronic viral hepatitis. Ann Trop Pathol 2012;3:85‑91.
5. Zein N. The epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis C virus infection. Cleveland Clinic J Med 2003;70:1‑6.
6. Karoney MJ, Siika AM. Hepatitis C virus infection in Africa: A review. Pan Afr Med J 2013;14:44.
7. Saleh HA, Abu‑Rashed AH. Liver biopsy remains the gold standard for evaluation of chronic hepatitis and fibrosis. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2007;16:425‑6.
8. Scheuer PJ. Liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis: 1968‑78. Gut 1978;19:554‑7.
9. Hübscher SG. Histological grading and staging in chronic hepatitis: Clinical applications and problems. J Hepatol 1998;29:1015‑22.
10. Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1981;1:431‑5.
11. Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 1995; 22:696‑9.
12. Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: A need for reassessment. J Hepatol 1991;13:372‑4.
13. Batts KP, Ludwig J. Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1409‑17.
14. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The French METAVIR cooperative
study group. Hepatology 1994;20:15‑20.
15. BruntEM. Grading and staging the histopathological lesions of chronic hepatitis: The Knodell histology activity index and beyond. Hepatology
2000;31:241‑6.
16. Terminology of chronic hepatitis, hepatic allograft rejection, and nodular lesions of the liver: Summary of recommendations developed
by an international working party, supported by the world congresses of gastroenterology, Los Angeles, 1994. Am J Gastroenterol 1994; 89:S177‑81.
17. Goodman ZD. Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 2007;47:598‑607.
18. Desmet VJ. Milestones in liver disease; scoring chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 2003;38:382‑6.
19. Samaila AA, Mohammed AZ, Borodo MM, Tijjani BM. Histopathological findings in liver biopsies and clinical correlation at Kano, Nigeria. Sahel Med J 2008;11:20‑3.
20. Samuel DO, Oluleke IP, Omotara SM. Safety of liver biopsy as a day procedure in ABUTH Zaria, Nigeria. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2012; 22:675‑6.
21. Laraba A, Wadzali G, Sunday B, Abdulfatai O, Fatai S. Hepatitis C virus infection in Nigerians with chronic liver disease. Int J Gastroenterol
2010;9:9-13. [doi: 10.5550/1775].
22. Echejoh GO, Tanko NM, Manasseh AN, Mandong BM, Ogala‑Echejoh SE, Ladep GN, et al. Clinicopathological correlation of liver biopsy in Jos, central Nigeria. Jeune Chambre Commer Montr 2007;10:557‑62.
23. Ugiagbe EE, Udoh MO. The histopathological pattern of liver biopsies at the university of Benin teaching hospital. Niger J Clin Pract 2013; 16:526‑9.
24. Abdulkareem FB, Banjo AA, Elesha SO, Daramola AO. Histopathological study of liver diseases at the Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Nigeria (1989‑2000). Niger Postgrad Med J 2006;13:41‑65.
25. Mbaawuaga EM, Iroegbu CU, Ike AC. 2014 hepatitis B virus serological patterns in Benue State, Nigeria. Open J Med Microbiol 2014;4:1‑10.
26. Musa BM, Bussell S, Borodo MM, Samaila AA, Femi OL. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in Nigeria, 2000‑2013: A systematic review and meta‑analysis. Niger J Clin Pract 2015;18:163‑72.
27. Hytiroglou P, Snover DC, Alves V, Balabaud C, Bhathal PS, Bioulac‑Sage P, et al. Beyond “cirrhosis”: A proposal from the international liver pathology study group. Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:5‑9.
28. Okafor O, Ojo S. A comparative analysis of six current histological classification schemes and scoring systems used in chronic hepatitis
reporting. Rev Esp Patol 2004;37:269‑77.
29. Manuyakorn A, Tanwandee T, Atisook K. Pathologically different features and fibrosis scores in chronic hepatitis C genotypes 3 and 1.
J Med Assoc Thai 2007;90:1123‑8.
30. AnwarAA, KhaliqulRS, Syed Qaiser HN, Mustafa K. Histopathological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis C patients in rural Sindh. J Liaquat Univ Med Health Sci 2009;8:121‑5.
31. Silva GF, Nishimura NF, Coelho KI, Soares EC. Grading and staging chronic hepatitis C and its relation to genotypes and epidemiological
factors in Brazilian blood donors. Braz J Infect Dis 2005;9:142‑9.
32. Atiqur MD, Sultana RM. Degree of viraemia and liver histology in chronic hepatitis C. Anwer Khan Mod Med Coll J 2010;1:17‑20.