Urethral prolapse: An important differential diagnosis of bleeding from the vulva in pre‑pubertal African girls
Main Article Content
Abstract
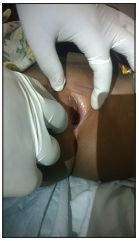
Urethral prolapse is the abnormal protrusion of the urethral mucosa through the external urethral meatus. It is a rarely diagnosed condition as most cases will be misdiagnosed as sexual abuse. If diagnosed, however, medical treatment with follow-up will usually suffice. If this fails, or in the presence of complications, surgical management may be employed. The most common presenting feature is urogenital bleeding. Genital bleeding in a pre-pubertal child is alarming to parents. Their first impression is that of a sexual abuse resulting in the suspicion of all adult males in the surrounding environment. The condition is worsened by a scenario in which the child is either too little to give an account or where she points accusing fingers to some adults. We report a case of bleeding from the vulva from urethral prolapse masquerading as suspected sexual abuse from an unknown adult.
Downloads
Article Details
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1. Urethral Prolapse. Available from: http://www.emedicine. medscape.com/article/443165‑treatment#showall. [Last accessed on 2015 Sep 11].
2. Anveden‑Hertzberg L, Gauderer MW, Elder JS. Urethral prolapse: An often misdiagnosed cause of urogenital bleeding in girls. Pediatr Emerg Care 1995;11:212‑4.
3. Shavit I, Solt I. Urethral prolapse misdiagnosed as vaginal bleeding in a premenarchal girl. Eur J Pediatr 2008;167:597‑8.
4. Fiogbe MA, Hounnou GM, Koura A, Agossou‑Voyeme KA. Urethral mucosal prolapse in young girls: A report of nine cases in Cotonou. Afr J Paediatr Surg 2011;8:12‑4.
5. Pouya M, Van Cangh PJ, Wese FX, Opsomer RJ, Saleh M. Mucous prolapse of the urethra. Acta Urol Belg 1995;63:23‑9.
6. Urethral Prolapse. Division of Urology, The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Available from: http://www.chop.edu/conditions‑diseases/urethral‑prolapse#.VfL1dn2cUdU. [Last accessed on 2015 Sep 11].
7. Holbrook C, Misra D. Surgical management of urethral prolapse in girls: 13 years’ experience. BJU Int 2012;110:132‑4.
8. Falandry L. Prolapse of the urethra in black girls. Personal experience in 11 cases. Med Trop (Mars) 1994;54:152‑6.
9. ValerieE, GilchristBF, FrischerJ, ScrivenR, KlotzDH, RamenofskyML, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of urethral prolapse in children. Urology
1999;54:1082‑4.
10. Shurtleff BT, Barone JG. Urethral prolapse: Four quadrant excisional technique. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2002;15:209‑11.
11. Johnson CF. Prolapse of the urethra: Confusion of clinical and anatomic characteristics with sexual abuse. Pediatrics 1991;87:722‑5.
12. Vunda A, Vandertuin L, Gervaix A. Urethral prolapse: An overlooked diagnosis of urogenital bleeding in pre‑menarcheal girls. J Pediatr 2011; 158:682‑3.
13. Kisanga RE, Aboud MM. Urethral mucosa prolapse in young girls. Cent Afr J Med 1996;42:31‑3.
14. Richardson DA, Hajj SN, Herbst AL. Medical treatment of urethral prolapse in children. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:69‑74.
15. da Silva‑Anoma S, Bertin KD, Ossenou O, Gaudens DA, Yao D, Roux C, et al. Prolapse of the urethral mucosa in young girls from the ivory coast. Ann Urol (Paris) 2001;35:60‑3.
16. Jiménez Parra JD, CebriánLostal JL, Lozano Uruñuela F, Alvarez Bandrés S. Urethral prolapse in postmenopausal women. Actas Urol Esp 2010;34:560‑72.
17. Wong HY, Tsui SY, Mou WC, Lee KH. Blood spotting on underpants: Case report of urethral prolapsed in a pre‑pubertal Chinese girl. J Paediatr Surg 2015;3:192‑3.