Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose among Persons Living with Diabetes Mellitus in a Tertiary Hospital in Southern Nigeria
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Self-monitoring of blood glucose is a critical part of diabetes management. It promotes personal responsibility, provides opportunities for better control and allows for detection of blood glucose extremes, while reducing fluctuations. It also helps both the patient and the provider make informed decisions and potentially reduces complications. Studies have shown that haemoglobin A1c levels are lower if glucose is tested more frequently.
Aim: To determine the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose, among patients living with diabetes mellitus in a tertiary Hospital in Southern Nigeria.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of 85 patients attending the medical outpatient clinic of University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital in 2023 using a self-administered questionnaire. Data was analysed using the SPSS version 26.
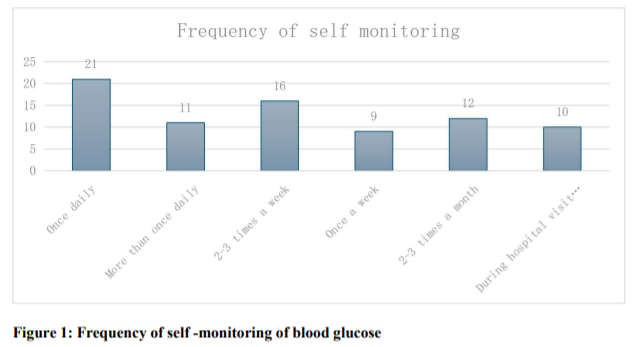
Results: A total of eighty-five (85) patients between the ages of 20 to 80 years were recruited, 34(69%) were females and 26 (31.0%) were males. Of all participants 73.5% owned a glucometer and 26.5% didn't own one. Only 79% performed self-monitoring of blood glucose while 21% did not perform it. Slightly above a quarter checked their blood glucose once daily (26.6%), 13.9% checked more than once a day, 11.4% checked once a week and others checked less frequently.
Conclusion: The frequency of practise of self-monitoring of blood glucose was higher (79%) than previous studies. Over a quarter 26.6% checked daily and 13.9% checked more than once a day. Persons living with diabetes mellitus should be encouraged to practise individualised SMBG to achieve better glycaemic control and have better outcomes.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
Nwafor CE, Edeogu J, Stanley R, Enyichukwu B, Ogomegbunam M. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus among adult population within a Southern Nigerian community. Eur J Med Health Res 2024;2(1):131-137.
Cookey SN, Gomba V, Wariboko CM. Prevalence of diabetes in rural communities in South South and South East Nigeria: a retrospective, cross sectional community based survey. IOSR J Dent Med Sci 2022;21(2):26-32.
Salome CO, Ordinioha B, Penuel A, Fente AE, Clement TY. Diabetes and its associated factors among oil and gas company workers in Port Harcourt. Saudi J Med 2023;8(11):596-614.
Unachukwu CN, Uchenna DI, Young E. Mortality among diabetes in-patients in Port-Harcourt, Nigeria. Afr J Endocrinol Metab 2008;7(1):1-4.
Mshelia-Reng R, Lawal Y, Adediran O, Anumah FE. The prevalence of the practice of self-monitoring of blood glucose and association with glycemic control: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary hospital in North Central Nigeria. South Asian Res J Med Sci 2024;6(2):20-24.
Klimek M, Knap J, Reda M, Masternak M. History of glucose monitoring: past, present, future. J Educ Health Sport 2019;9(9):222-227.
Pleus S, Freckmann G, Schauer S, Heinemann L, Ziegler R, Ji L, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as an integral part in the management of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther 2022;13(5):829-846.
Otokunefor O, Ogu R. Comparing the glucose results by glucometer and laboratory methods: a prospective hospital based study. J Adv Med Med Res 2018;26(3):1-7.
Geetha P, Vishakha K, Pooja S, Vyshnav M. Comparative study on venous and capillary blood collection for estimation of glucose. SALT J Sci Res Healthc 2021;1(2):13-23.
Iqbal HB, Kashif M, Hamid Y, Hayat T, Bilal. Comparison of results of glucometer and laboratory technique for glucose measurement among children. Medtigo J Med 2024;2(4):e30622411.
Lakshmi N, Kiranmai P. A comparative study of blood glucose level measurement between glucometer and semi autoanalyser. Int J Clin Biochem Res 2018;5(3):423-426.
Rinzo L. Self-monitoring blood glucose: A vital tool for effective diabetes management. Diabetes Manag 2024;14(3):621–622.
Kirk J, Stegner J. Self-monitoring of blood glucose: practical aspects. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2010;4(2):435-439.
Bergenstal R, Gavin JR 3rd; Global Consensus Conference on Glucose Monitoring Panel. The role of self-monitoring of blood glucose in the care of people with diabetes: report of a global consensus conference. Am J Med 2005;118(suppl 9A):1S-6S.
Lowe J. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes. Aust Prescr 2010;33(5):138-141.
WHO. Guidance on global monitoring for diabetes prevention and control. Framework, indicators and application. Geneva:World Health Organization, 2024;1-94. Available online @ https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/ncds/ncd-surveillance/guidance-on-global-monitoring-for-diabetes.pdf?sfvrsn=ccb261b8_4. Accessed 3rd April, 2025.
Adeleye O, Ogbera A, Ugwu E, Brodie-Mends A. Impact of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetic Nigerians who reside in Lagos. Open Diabetes J 2019;9(1):1-7.
Ugwu ET, Orjioke CJG, Young EE. Self monitoring of blood glucose among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Eastern Nigeria: need for multi-strategic interventions. Curr Diabetes Rev 2018;14(2):175-181.
Zeng Y, Wu J, Han Y, Chen F, Chen L, Yang S, et al. Educational disparities in the associations between self-monitoring of blood glucose and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients in Xiamen, China. J Diabetes 2018;10(9):715-723.
Klonoff DC. Benefits and limitations of self-monitoring of blood glucose. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2007;1(1):130-132.
Schnell O, Alawi H, Battelino T, Ceriello A, Diem P, Felton AM, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: recent studies. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2013;7(2):478-488.
Sia HK, Kor CT, Tu ST, Liao PY, Wang JY. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in association with glycemic control in newly diagnosed non-insulin-treated diabetes patients: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep 2021;11(1):1176.
Kemp T. Routine monitoring of diabetes mellitus in adults at primary health care level, and self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG). Contin Med Educ 2010;28(10):452-457. Benjamin EM. Self-monitoring of blood glucose: the basics. Clin Diabetes 2002;20(1):45–47.