Histopathological results of nasopharyngeal masses of adult patients: a study from two centres in Port Harcourt, Nigeria
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background:
Methods: clinical features, investigations, histopathological findings, treatment, complications and management outcome Nasopharyngeal masses in adult patients in most cases are considered to be tumours unless proven otherwise.
Aim: To determine the histopathological results of nasopharyngeal masses seen in adult patients in Port Harcourt Nigeria. It will also highlight the management outcomes of these patients.
Method: A prospective (January 2010 to December 2013) study of 45 patients with both clinical and radiological evidence of nasopharyngeal masses seen at the Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) surgery clinics of University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital (UPTH) and Kinx Medical Consultants clinic in Port Harcourt. All the patients had examination under anaesthesia (E/U/A) of the nose and nasopharynx and biopsy. The data collected were documented in a proforma designed for the study by the researchers. The data are bio-data, . The data were entered into an SPSS version 14 computer soft ware and analyzed descriptively.
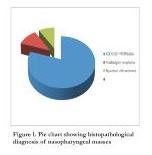
Results: Forty five adult patients had E/U/A of the nose and nasopharynx and biopsy of nasopharyngeal masses. They all had history of chronic rhinorrhoea, snoring and nasal obstruction. Age range was 18-72 years. There were 20 males and 25 females with male to female ratio of 1:1.25. The commonest histopathological diagnosis was adenoidal hyperplasia (n=36, 80%) followed by non-Hodgkin lymphoma (n=5, 11.11%).
Conclusion: Even though the predominant histopathological result of nasopharyngeal masses in adult patients we encountered was adenoidal hyperplasia, all tissues from the nasopharynx irrespective of their benign macroscopic appearances should be subjected to histopathological examination to avoid missing out more sinister diagnosis.
Downloads
Article Details
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1.Wysocka J, Hassmann E, Lipska A, Musiatowicz M. Naive and memory T cells in hypertrophied adenoid in children according to age. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2003; 67: 237-241.
2 Karodpati N, Shinde V, Deogawkar S, Ghate G. Adenoid hypertrophy in adults - a myth or reality. Webmed Central Otorhinolaryngology 2013; 4:WMC004079.
3 Orji F, Okorafor I, Ofoegbu V, Ilechukwu I A. Obstructive adenoid hypertrophy in the adult: a case report. Orient J Med 2009; 21:20-24.
4 Mitchell J, Pai I, Pitkin L, Moore-Gillon V. A case for biopsying all adult adenoidal tissue. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2008; 9(2).
5 Kamel RH, Ishak EA. Enlarged adenoid and adenoidectomy in adults: endoscopic approach and histopathological study. J Laryngol Otol 1990; 104: 965-967.
6 Huang H M, Chao MC, Chen YL Hsiao HR. A combined method of conventional and
endoscopic adenoidectomy. Laryngoscope 1998; 108:1104-1106.
7 Wan YM, Wong KC, Ma KH. Endoscopicguided adenoidectomy using a classic adenoid
curette: a simple way to improve adenoidectomy. Hong Kong Med J 2005; 11:42-44.
8 Schaffer SR, Wong GH. Endoscopic visualization facilitates adenoidectomy.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2007; 136:510.
9 Rout MR, Mohanty D, Vijaylaxmi Y, Bobba K, Metta C. Adenoid hypertrophy in adults: a case series. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2013; 65:269-274.
10 Finkelstein Y, Ophir D, Talmi YP, Shabtai A, Strauss M, Zohar Y. Adult-onset otitis media with effusion. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg1994; 120:517-527.
11 Nwaorgu OG, Ogunbiyi JO. Nasopharyngeal cancer at the University College Hospital Ibadan Cancer Registry: an update. West Afr J Med 2004; 23: 135-138.
12 da Lilly Tariah OB, Somefun AO. Malignant tumours of the nasopharynx at Jos University Teaching Hospital, Nigeria. Niger Postgrad Med J2003; 10: 99-102.
13 Yildirim N, Sahan M, Karslioglu Y. Adenoid hypertrophy in adults: clinical and morphological characteristics. J Int Med Res 2008; 36: 157-162.
14 Moazzez AH, Alvi A. Head and neck manifestations of AIDS in adults. Am Fam Physician 1998; 57: 1813-1822.