Aerodigestives foreign bodies: Clinical profile and management
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Upper aerodigestive foreign bodies are a common occurrence in otorhinolaryngologic practice. We present our experience with the management of upper aerodigestive foreign bodies over a 5-year period at the Ear, Nose and Throat Department of the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Benin City, Nigeria.
Methods: A retrospective review of medical records and theatre documents of patients presenting with aerodigestive foreign bodies between January 2010 and December 2014 were carried out.
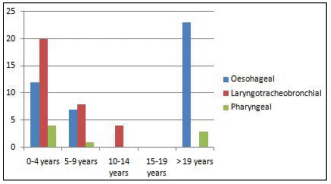
Results: A total of 82 cases of aerodigestive foreign bodies were seen comprising of 53 males and 29 females in a ratio of 1.8:1. Age ranged from 9 months to 85 years. The group most at risk of aerodigestive foreign bodies are those aged between 0 and 4 years. Common foreign bodies were parts of toys, fishbone and groundnut in children and dentures and fishbone in adults.
Conclusion: Aerodigestive foreign bodies are a common occurrence especially in the paediatric age group. Early detection and removal can forestall complications.
Downloads
Article Details
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1. Mahafza TM. Extracting coins from the upper end of the esophagus using a Magill forceps technique. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2002; 62: 37‑9.
2. Wai Pak M, Chung Lee W, Kwok Fung H, van Hasselt CA. A prospective study of foreign‑body ingestion in 311 children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2001;58:37‑45.
3. Gupta P, Jain AK. Foreign bodies in upper aero‑digestive tract: A clinical study. Int J Res Med Sci 2014;2:886‑91.
4. Phillipps JJ, Patel P. Swallowed foreign bodies. J Laryngol Otol 1988;102:235‑41.
5. Okeowo PA. Foreign bodies in pharynx and oesophagus – A 10 year review of patients seen in Lagos. Niger Quart J Hosp Med 1985;3:46‑50.
6. Nwaorgu OG, Onakoya PA, Sogebi OA, Kokong DD, Dosumu OO. Esophageal impacted dentures. J Natl Med Assoc 2004;96:1350‑3.
7. Asif M, Haroon T, Khan Z, Muhammad R, Malik S, Khan F. Foreign body in oesophagus: Types and sites of impaction. Gomal J Med Sci
2013;11:163‑6.
8. Alabi BS, Oyinloye OI, Omokanye HK, Dunmade AD, Afolabi OA, Akande HJ. Foreign bodies in the upper aerodigestive tract of Nigerian
children. Nigeria J Surg 2011;17:78‑81.
9. Onyeagwara NC, Okhakhu AL, Emokpaire E, Ogisi F. Dynamics in the trend of foreign bodies in ENT practice in Nigeria: Any change? Internet J Otorhinolaryngol 2012;14:2.
10. Reilly JS, Cook SP, Stool D, Rider G. Prevention and management of aerodigestive foreign body injuries in childhood. Pediatr Clin North Am 1996;43:1403‑11.
11. Iseh KR, Oyedepo OB, Aliyu D. Pharyngo‑oesophageal foreign bodies: Implication for health care services in Nigeria. Ann Afr Med 2006;5:52‑5.
12. Onotai LO, Ibekwe MU. A survey of upper aerodigestive tract emergencies seen in a Nigerian tertiary hospital. Int J Med Sci 2012;2:92‑6.
13. Gilyoma JM, Chalya PL. Endoscopic procedures for removal of foreign bodies of the aerodigestive tract: The Bugando medical centre experience. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2011;11:2.
14. Afolabi OA, Okhakhu AL, Adeosun AA. Re‑emergence of coin in Nigerian currency: Implication in medical practice. Internet J Otorhinolaryngol 2008;9:1.
15. Kamath P, Bhojwani KM, Prasannaraj T, Abhijith K. Foreign bodies in the aerodigestive tract – A clinical study of cases in the coastal belt of South India. Am J Otolaryngol 2006;27:373‑7.
16. Kirfi AM, Mohammed GM, Abubakar TS, Labaran AS, Samdi MT, Fufore MB. Clinical profile and management of aerodigestive foreign bodies in North –Western Nigeria. Sudan Med Monit 2014;9:39‑43.
17. Baraka A, Bikhazi G. Oesophageal foreign bodies. Br Med J 1975;1:561‑3.